What is Joint pain?
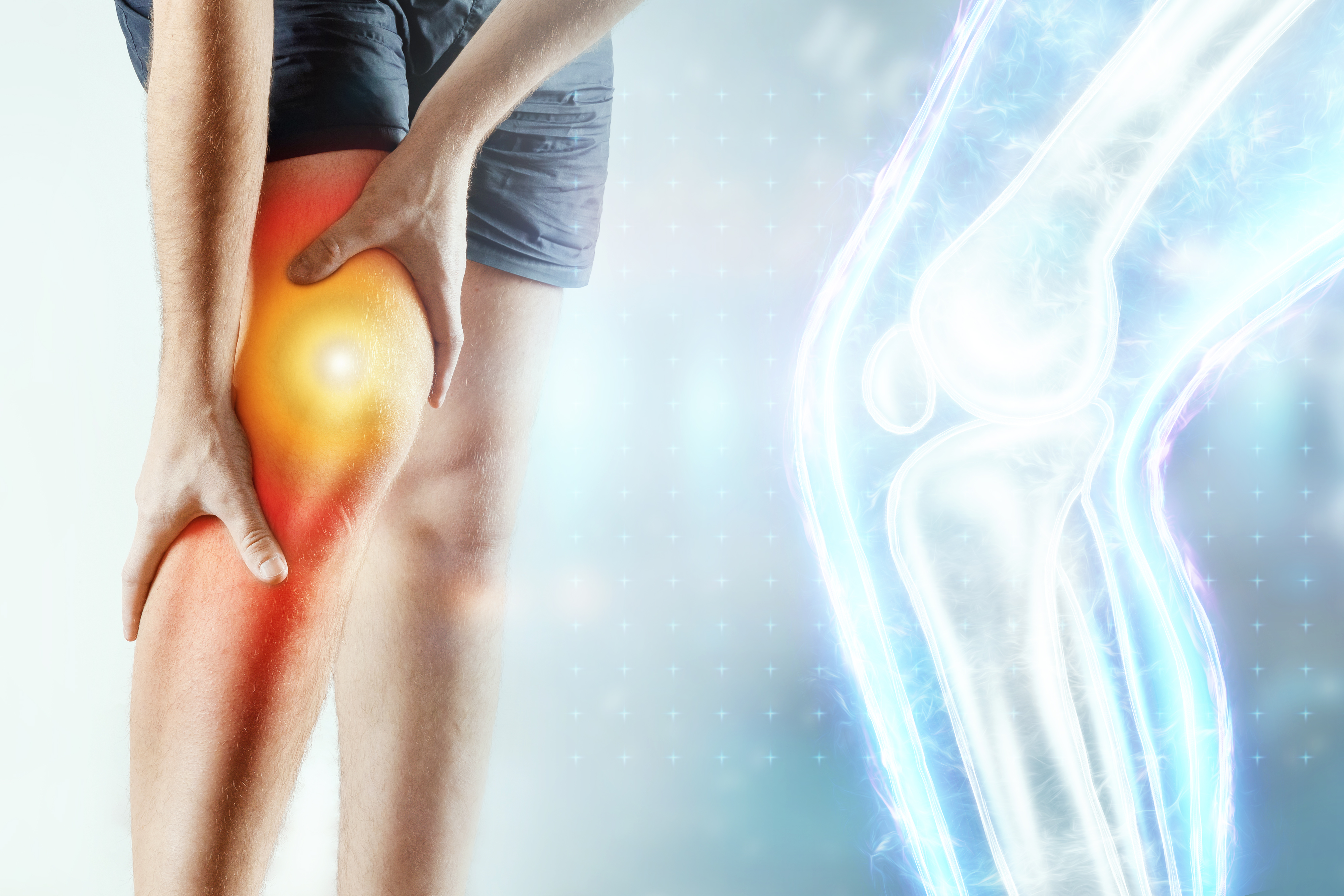
Joint pain is a widespread issue that can affect people of all ages. There are numerous causes of joint pain, ranging from injuries to arthritis. Pain or discomfort in one or more of your joints characterises joint pain. It could be a temporary or permanent condition. Among the most common issues are pain and soreness while moving.
In this blog post, we will discuss joint pain in more detail and provide tips on managing it.
Joints pain as per Ayurveda
Joint pain can be often caused due to the imbalance of vata in the body. Vata dosha is free-flowing energy that circulates through all parts of the body. It is imbalanced when it goes inside bones causing increased stiffness, pain and irritation. The vitiated pitta results in joint inflammation while aggravated vata plays important role in the overall cascade of joint pain.
Vyana vayu is thought to be in charge of joint motion, whereas Apana vayu is thought to be in charge of bone health. Therefore, we can conclude that vyana vayu is responsible for disrupted motion, whereas Apana vitiation is responsible for joint destruction. Synovial fluids are also attributed to Sleshaka Kapha, whose vitiation causes an excess of fluid to accumulate, causing swelling in the joint.
Ayurveda considers any deviation from the natural movement of doshas can result in disorders or diseases. Ayurveda also considers vata dosha as causal for joint pain. Vata is responsible for the production of air and hence it gets settled in bones causing stiffness and pain.
Related causes as per Ayurveda
There are numerous issues that interfere with the normal functioning of the joints, leading to the emergence of various diseases. Injury from trauma is one of the issues that contribute to decreased joint function, but inflammation and degeneration are the primary causes of joint dysfunction.
- Too much ama or toxic mucous created from the indigested food due to low digestive power gets settles in the bones causing stiffness and tightness or swelling in the affected area.
- Vata imbalance can be aggravated by eating too many foods that are chilly, dry, bitter, or pungent, living an erratic lifestyle, travelling too much, experiencing stress, getting too little sleep, experiencing a traumatic experience, and having certain genetic characteristics. The most sensitive parts of the body, such as the joints, are affected by the increased Vata and Ama or toxins as they travel into the srotas or bodily channels.
Symptoms / Common signs of joint pain
- Stiffness accompanied by acute pain in any one of the joints viz knee, finger, shoulder, back etc.
- Pain ranging from moderate to severe in the affected joint
- Joint stiffness, particularly after long periods of rest for the affected joint, restricted and painful joint movements crunching or crackling crackling loud sounds when the joint moves
- In severe cases, there may be localised tenderness.
- Swelling around the affected joint
- The affected site's local temperature has risen.
- Cracking sound or crepitus from the joints, especially the knee.
- Pain due to muscle stiffness and tightness.
- Throbbing or pulsating pain over the nerves.
Treatment as per Ayurveda
Joint pain can often be debilitating, making it difficult to carry out everyday activities. There are several treatments available for joint pain, depending on the underlying cause. Ayurvedic treatment of joint pain is based on the theory that vitiation of vata dosha or the quality of air in the body causes pain. This is known as Vata-dosh-pitta (vitiation). The best way to treat your joint pain is to adjust the dosha, which will reduce pain and inflammation and help you recover fast.
Ayurvedic joint pain treatment is based on understanding the dosha and treating each dosha separately.
- The fundamental course of treatment entails restoring balance to vitiated elements like agni or digestive fire, ama or removal of toxins accumulated, and vata dosha balance.
- Many conventional herbal compositions were suggested by Ayurveda, a system of natural medicine, for the management of disorders including joint discomfort. These medications aid in reducing joint pain, stiffness, soreness, and oedema. Additionally, the herbal remedy has the power to calm down agitated Vata and ama.
- Rasayana formulations hydrate the Ojas and nourish joint tissues. The ayurvedic drug not only balances toxins and doshas but also improves digestive fire function, which lessens joint pain in its early phases.
Diet as per Ayurveda
- Vata pacifying diet
- A moderate diet which helps to pacify vata dosha is primarily best to cure joint pain.
- Avoid dry,
- Include the following food items in the diet
- Rice, roti, bhakahris made of bajra, jowar, ragi.
- Pulses like moong dal, masoor dal, tuvar dal
- Vegetables like pumpkin, karela, carrot, beetroot, coriander, onion, fenugreek, zucchini, artichoke, squashes, celery, spinach, melon and cantaloupe.
- Spices like ginger, garlic, clove, cinnamon,
- Fruits like avocado, apricot, sweet apple, sweet grapes, banana, coconut, rye amaranthus, figs, dates, melons, papaya
- Avoid following food items
- Avoid sour food items like curd, imli, grain-like wheat & all wheat products, oily food, raw salad, red meat, and fermented food items like idli, dosa etc.
- Avoid gas-forming food items like rajmah, white chickpea, dry peas, frozen peas, and white beans.
- Avoid vegetables like bhindi, brinjal, fansi or french beans, and raw mango.
- Avoid beverages like chilled water, aerated drinks, cold milk and ice cream.
Natural ways to cure joint pain
- Know the cause
- The best way is to have a better understanding of the disease and its causes, as well as manage your activities appropriately.
- In addition to physical treatment, rest, hot and cold packs, and herbal supplements can be used.
- Be active to reduce pain
- When you have joint pain, the first thing to do is soothe the area with gentle exercise and gentle movement that includes cycling and swimming, as well as walking, jogging, and strengthening.
- Include herbal supplements
- Heal your joint pain naturally by maximizing your intake of vitamin D, Turmeric and Omega-3 supplements.
- Lifestyle recommendations
- To lessen the strain on your joints, if you are overweight, control your weight.
- Increase your vitamin D levels by getting more sun exposure to strengthen your bones.
- Use warm sesame oil or mustard oil that has been infused with powdered camphor to massage the affected areas.
- Consult the Expert
- The first and most important step to helping relieve your pain is getting an accurate diagnosis from your doctor. With this information, you can begin treatment to relieve the joint pain caused by arthritis.
Herbs to cure joint pain
Ayurvedic herbal remedies for arthritis are numerous. These plants have anti-inflammatory properties without the negative side effects associated with commonly prescribed medications. With a herbal approach, Ayurveda provides safe and effective treatment alternatives. Single herbs such as Boswellia, turmeric, ashwagandha, ginger, Triphala, Guggulu, and Shatavari have all been shown to reduce inflammation by interfering with the body's production of inflammatory chemicals.
Yoga to cure joint pain
Yoga can be extremely beneficial in alleviating joint pain. It improves blood circulation to the joints, which reduces inflammation and facilitates mobility such as;
- Virabhadrasana/Warrior pose
- Vrikshasana /Tree Pose
- Trikonasana/ Triangle Pose
- Setubandhasana or Bridge Pose
- Marjariasana/ Cat Stretch: Urdhva Mukhi Marjari Asana, Adho Mukhi Marjari Asana
Conclusion
Ayurveda has been shown to cure joint pain, through its herbal management approach, in conjunction with other therapies as needed. Ayurveda has focused on causative factors such as physiological, metabolic, excretory, and mental functions, lifestyle, food patterns, and other factors that contribute to the development and progression of arthritic pain. Ayurvedic treatment aims to not only monitor symptoms but also to prevent disease progression, reduce impairment, improve quality of life, and address the aforementioned causative factors.